Salivary Mucocele in Dogs: Dogs have many salivary glands inside the oral cavity and in the head and neck area.
The most important salivary glands are
- Zygomatic (located near the eye)
- Mandibular (located behind the jaw bone)
- Sublingual (located below the tongue)
- Parotid salivary glands (located around the ear canal)
Causes of salivary mucocele in dogs
The inducing cause of salivary mucus is usually not precisely identified;
However, injury from a choke chain, bite to the neck and sudden hypertension of the neck are suspicious causes.

These cause the salivary gland or gland to stretch or rupture the duct that carries saliva from the mouth to the mouth.
Saliva accumulates under the skin and triggers a noticeable inflammatory response. The body tries to retain the leaked saliva by creating a layer of connective tissue around the saliva called the mucocele.
Signs and diagnosis for salivary mucocele in dogs
Mucoceles cells are found mainly in dogs and rarely in cats. mucoceles are more common in dachshunds, German shepherds, poodles, and silky terriers. They can occur at any age.
Also Read: Dogs with Pink Noses: why do dogs have pink noses?
Clinical signs associated with mucoceles depend on the affected gland:
Cervical mucoceles is caused by damage to the mandibular or sublingual salivary glands or the vessels associated with them.
Swelling is usually seen on the side or under the neck.
The pharyngeal mucoceles usually does not have externally visible inflammation because the accumulation is in the back of the throat and makes it difficult to breathe.
It is caused by damage to the mandibular or submandibular salivary glands or the vessels associated with them.
Anesthesia is required to allow examination of the throat to make a diagnosis.
The sublingual mucoceles is also called the ranula and is an inflammation under the tongue. This type of mucus is caused by damage to the sublingual vessels of the sublingual salivary gland.
Damage to the zygomatic mucoceles causes inflammation under the eye.
Other causes of inflammation in the neck include inflammation of the salivary gland, salivary gland tumors, infection with a lump in the neck due to a foreign body, enlarged lymph nodes and thyroglossal cyst, cystitis or cystitis.
Prior to surgery, the needle of the swollen aspirate and the fluid under the microscope should be examined.
In addition, blood work such as a complete blood count and chemistry profile is routinely performed to assess internal organ health status in the preparation of anesthesia and surgery.
Treatment for Salivary Mucocele in Dogs
Conventional treatment is a wait-or-see procedure or drainage of fluid from the cyst rarely leads to a solution to the problem.
Surgical removal of the salivary glands involved is the treatment of choice for a permanent cure of the problem.
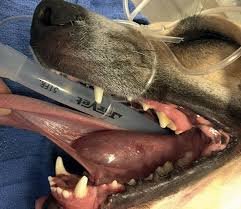
Although there are many important vessels and nerves around the gland that controls the movement and swallowing of the tongue, damage to these at the hands of an experienced surgeon is quite uncommon.
At the surgeon’s decision, a drain may be placed after the glands have been removed.
Removing a set of salivary glands impairs the ability to produce enough saliva because other glands take over the function.
Salivary Mucocele Dog Surgery Cost
A salivary mucocele is a benign growth on the mucous membranes that line the lower part of the throat. It most often occurs in dogs, but can also occur in cats.
The growth is typically less than 1 cm in diameter and does not usually cause any symptoms. If the mucocele becomes large or causes difficulty swallowing or breathing, it may need to be surgically removed.
If the tumor is caught early, it can usually be removed through surgery. The cost of this surgery will depend on the specific circumstances of the case, but typically it is not very expensive.
The cost of salivary mucocele surgery typically ranges from $250 to $1,000. The surgery is often necessary to correct a swollen or lumpy salivary gland, which can cause problems with swallowing, speaking, and chewing.
Almost all dogs are cured from salivary mucoceles by just one surgery.

