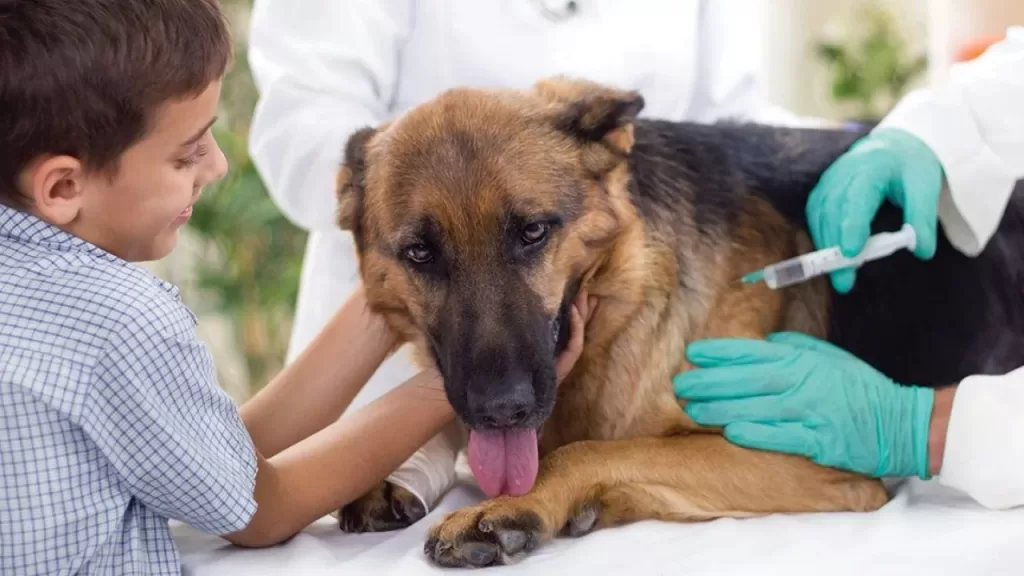
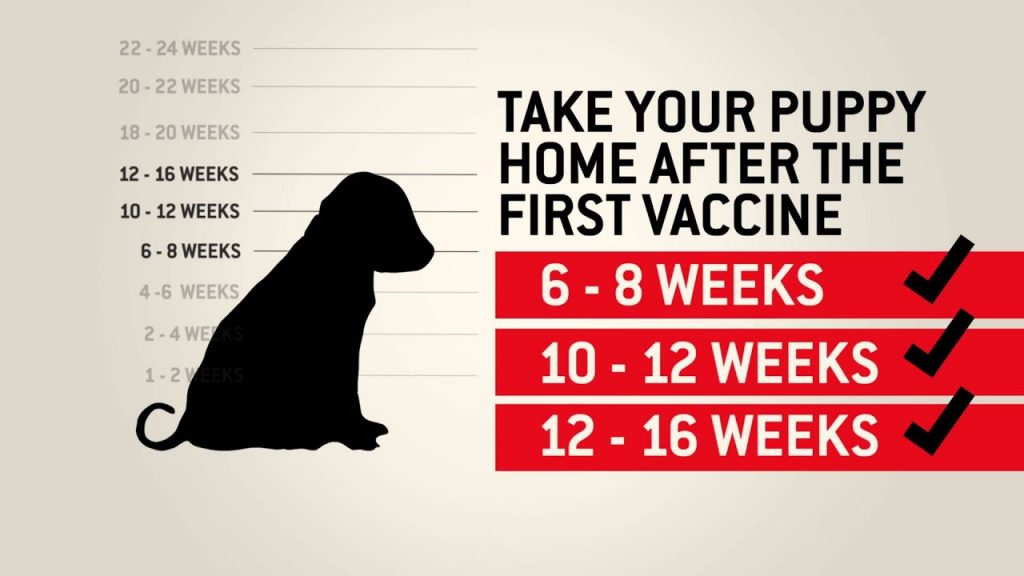
Vaccines are required for dogs to maintain a safe, comfortable environment, we want all pets to be present on their vaccinations and to wait at least 48 hours after being vaccinated before checking in at the groomer.
Table of Contents
Waiting a long time to make sure your pet is not feeling pain at the injected place on his body and can cause irritation or lethargy. This waiting period is also to prevent stress on the pet that is experiencing an unexpected allergic reaction from the vaccine.
Grooming makes our dogs look clean, neat and beautiful. It is an important part of their care routine and very important for their health, plus, they look so beautiful later!
However, some safety precautions need to be taken before vaccinating your dog specifically for bathing and haircut.
Vaccinating your dog ensures that your dog and other pups at Groomer are protected from the spread of deadly virus diseases. If dogs are not properly cared for, diseases can spread easily at Groomer, pet stores, and vet clinics.
Shots dogs need to get groomed
| DHLPP | DHPP / DHLPP: This is often referred to as a “distemper shot”. In fact, this combination vaccine shot can protect your dog from 4 different diseases. The acronym means distemper, hepatitis, parainfluenza, and parvovirus. |
| Bordetella | Puppies should receive an injected version of the Bordella vaccine between six and eight weeks of age. They should receive a second injection booster four weeks later or between 10 and 12 weeks. |
| Anti Rabies Vaccine | The rabies vaccine (Imovax) is a vaccine used to prevent rabies in people who have been bitten by an animal or who have been infected with the rabies virus. |
Bortedella (also known as “kennel cough”) is one of the most commonly needed vaccines for Groomers. The kennel cough is very contagious. If you keep your pet away from other dogs or in a special cage for the duration of the dressing session, still he or she will be at risk.
Bordetella can circulate in the air through coughing and sneezing or is transmitted directly from nose to nose. Though appropriate cleaning measures are taken, viral can be circulated in the environment and be transmitted to your pet.
Additional Dog Vaccines that are required for taking him to a professional groomer
Before visiting Groomer, your dog should be up to date on all core vaccines. Vaccine recommendations depend on your geographical location, as disease prevalence varies by region.
here is a chart on the list of vaccinations to be administered to dogs in the USA:
| Vaccine | Disease | Recommended Age |
|---|---|---|
| Core Vaccines | ||
| DHLPP | Canine distemper, hepatitis, leptospirosis, parvovirus, parainfluenza | 6-, 12-, 16 weeks old; then 1 year, and every 3 years thereafter |
| Rabies | Rabies | 12 weeks old; then every 1-3 years, depending on state law |
| Non-Core Vaccines | ||
| Bordetella | Kennel cough | 6-, 12-, 16 weeks old; then annually or every 6 months, depending on risk factors |
| Lyme disease | Lyme disease | 12 weeks old; then annually, depending on risk factors |
| Canine influenza | Canine influenza | 6-, 12-, 16 weeks old; then annually, depending on risk factors |
| Other Vaccines | ||
| Coronavirus | Coronavirus | 6-, 12-, 16 weeks old; then annually, depending on risk factors |
| Giardia | Giardia | 6-, 12-, 16 weeks old; then annually, depending on risk factors |
Notes:
- This is not an exhaustive list of all the vaccines that may be recommended for dogs.
- The recommended age and booster schedule may vary depending on the individual dog’s risk factors.
- It is important to talk to your veterinarian about the best vaccination schedule for your dog.
However, core vaccines (meaning that they are essential for your pet’s safety) usually include a combination of dog vaccines against the following diseases:
- Canine distemper virus
Virus canine distemper is a disease that affects the respiratory, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems of dogs, as well as the conjunctival membranes of the eye.
- Canine Parainfluenza
The Canine parainfluenza virus (CPIV) is a highly transmittable respiratory virus and is one of the most common pathogens of infectious trachobronchitis, also known as canine cough.
- Canine Adenovirus
There are 2 different and distinct adenoviruses that infect dogs. CAV-1 causes infectious hepatitis and upper respiratory disease, whereas CAV-2 mainly causes acute upper respiratory disease. CAV-2 is a viral agent found in the “kennel cough” complex of dogs.
- Canine Parvo Virus
Canine parvovirus is an infection that mainly affects dogs. CPV is highly contagious and is transmitted from dog to dog through direct or indirect contact with their feces. Vaccines can prevent this infection, but in untreated cases, the death toll can reach 91%. Canine Parvo Virus Treatment often involves visiting a veterinary hospital.
Dog grooming without Vaccinations
Dog grooming without vaccinations is risky and sometimes that can lead to danger. If your pet is not vaccinated and if proper proof is not taken along with you, Groomer will not groom your pet.
This approach is required to ensure the health and safety of your pet, other puppies who visit the same groomer as well.
Unvaccinated puppies and adolescent dogs are more susceptible to these viruses. They are usually at risk with unknown vaccine histories or purchased from pet stores.

